Title Tag SEO – How to Write Title Tags That Increase CTR
November 4th, 2016 by Kyle J. Larson
Did you know you could be losing tons of potential traffic by doing a poor job setting your title & description tags? Using the right keywords may be important, but the real key to a good title & description is focusing on what the user wants. These tags are your first impression to the world and need to convince them that your content is the best. This guide will help improve your title tag SEO and increase your traffic.
Why Title Tags & Descriptions are Important
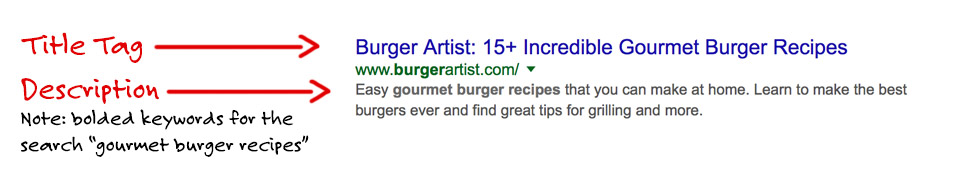
A title tag is what shows up as the large blue linked title when you do a Google search. This is the first thing that people will scan when deciding which link to click on. These are split-second decisions that people are making, so it’s absolutely critical to have a great title.
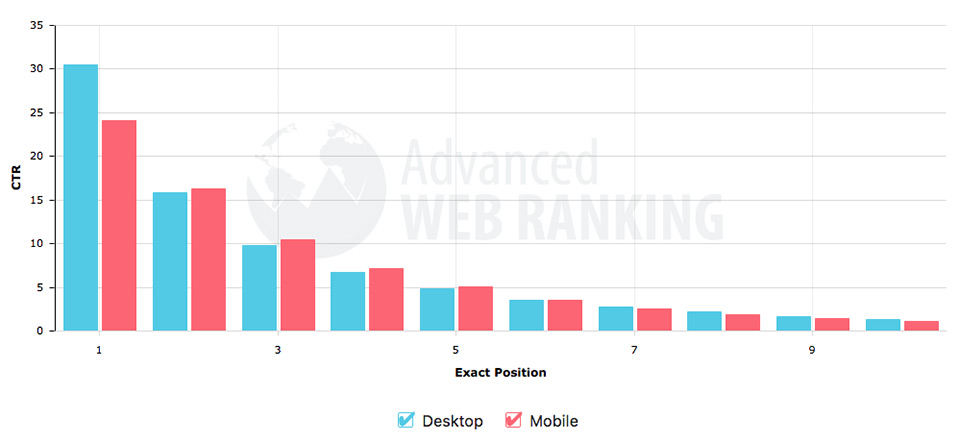
It’s been confirmed in the SEO world that click through rate does play some role in Google rankings. It makes sense that Google would drop a site from it’s top rankings if nobody clicked on it. They have tons of data to determine what click through rate to expect for each position in a search results list. If you can improve on your title tag SEO to outperform that number (or at least the competition) it makes sense that you’d eventually move up.
Take a look at this CTR chart from Advanced Web Ranking to get an idea of what to expect based a page’s rank.
A meta description may not be as important in a split-second decision, but they can still play a role in increasing your chances of being clicked. If a description isn’t set it’ll often become the first text on the page, and sometimes that first text is just a navigation menu which looks like garbage text in the results. That’d discourage anyone from clicking without an amazing title. Also, if two titles are similar but one has a description that is more interesting it’s likely to earn the click. Google is also bolding words from the user’s search so if you hit on those keywords it’ll make your page stand out.
How to Set Title Tags & Descriptions
These tags are pretty easy to setup in code or in WordPress. In WordPress most themes will automatically use your post or page title as the title tag. You can check this by opening your page in a web browser and seeing the text in the tab at the top (hover for a few seconds to see the full text). The description can be a little trickier to get set correctly so I’d recommend loading the Yoast SEO Plugin to control all of this.
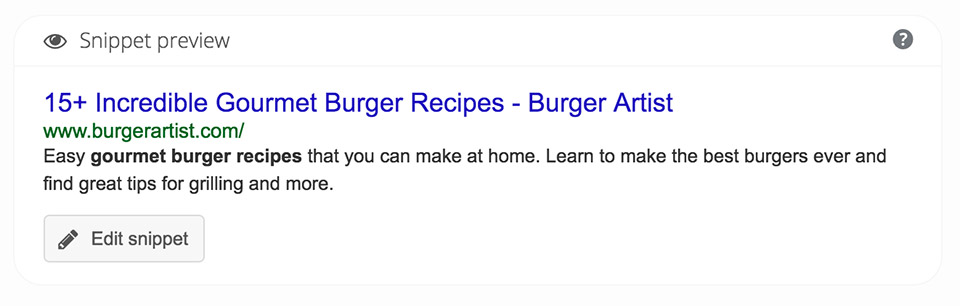
Yoast will add an SEO box right below your post or page content where you can edit the snippet. They display it like a Google search result which can help you visualize how it’ll look. Another great feature is you can make the title for your article different than the title tag that shows up in Google. Often you’ll want them to be the same, but it’s nice to have the option. For example on my burger recipe site I keep my titles simple like “Buffalo Chicken Burger”, but I set my title tag to something more interesting like “Buffalo Chicken Burger Recipe – Delicious & Spicy Burger Idea”.
In HTML you can add tags into the <head> section of your code to set the title & description tags.
A title tag looks like this:
<title>15+ Incredible Gourmet Burger Recipes</title>A description tag looks like this:
<meta
name="description" content="Easy gourmet burger recipes that you can make at home."/>Optimizing Title Tag SEO
Next, and most importantly, lets figure out how to set a good title tag. The first thing you’ll want to do is know what keywords you’re targeting. If you haven’t done much SEO before you’ll want to use a tool like Google Adwords or SEO PowerSuite to get an idea of what keywords are the most popular for your topic. In most cases you’ll want to include that phrase near the start of your title.
Check Out The Competition
Once you’ve identified a target keyword for the topic you’re writing on, try searching for that phrase. See who is currently ranking for it, and take a look at their titles and descriptions. Consider what is good or bad about them and how you can stand out. Some examples include:
- Out-do them: Do they have a title like “10 Great Ideas”? Maybe you can do “25 Great Ideas”
- Go negative: If the articles are all positive, maybe use the negative. Instead of “10 Great Diet Foods” maybe the article is “25 Diet Foods You Should Absolutely Avoid”
- Make it exciting: If most titles are informational, try adding excitement. “Home Experiments You Can Do With Your Child” vs “Amazing Home Experiments That Will Wow Your Child”
- Do the opposite: If their titles are all text, try using a number. If they are using lots of numbers try showing that you’re article is easier (e.g. ‘Easy…’, ‘Step-by-step guide to…’).
- Add a content descriptor: Can you add something to your content the others don’t have, or call out a specific feature? For example: “Infographic”, “Recipe”, “Video”, “Gallery”, “Slideshow”, “PDF”, “Updated for 2017”, “Review”. You can include these words at the end of the title or even add them in a [bracket] or (parentheses) to call it out.
Title Tag Examples
If you want to write good titles, it helps to check out a few sources where writing and testing titles are key to their business. You may not want to go overboard with the ‘clickbait’ style writing like “21 Horrible Things You Might Be Doing, You Won’t Believe #11!”, but there are still some good insights into what is working here:
BuzzFeed – King of clickbait articles. Some examples include:
- “23 Things That’ll Make Your Home Feel Like A Hotel”
- “Do You See Color Like Everyone Else?”
- “18 Celeb-Inspired Halloween Costumes That Totally Nailed It This Year”
- “11 Life Skills That Are Also Awesome Career Skills”
Business Insider – A little more ‘newsy’ but still very targeted article titles:
- “These are the best watches at every price point”
- “This iPhone 7 case has one of the coolest features I’ve ever seen”
- “The 7 biggest mistakes people make on college applications”
- “The 2 most important activities runners should do to avoid knee pain”
- “These are the 4 best sound bars you can buy”
Also try running a Google search and checking out the ads at the top or the side of the page. These are usually being tested to see which title gets the best click through rate.
Supporting the Title with Meta Description SEO
Now that you’ve got a great title it’s time to add a description. First off, you’ll want to include the key terms that you expect people to be searching for. These words will be bolded by Google so they’ll stand out and add proof that this article is relevant to their search.
In many cases your introductory paragraph to your article is a good place to start for this description. Similar to the intro, you’ll want to draw the reader into reading the rest of the article. Here are a few options to consider:
- Briefly summarize what content is going to be covered. Try to make this sound interesting or exciting: “The comprehensive guide to…”, “Learn the easiest way to…”, “The best method…”
- Add a hook sentence. “Don’t waste your time doing x… learn to do x instead!”, “x is so much easier once you’ve learned this simple 5 step trick.”, “10 methods you’ve never seen before”
- Expand on the title. Don’t repeat your title exactly, but try expanding it. If your title is “10 Easy to Make Gourmet Burgers” your description could be “These 10 gourmet burger recipes are super easy to make and amazingly delicious. Including step-by-step instructions to grill at home.”
Why is my description different in Google?
One thing to keep in mind when setting a description is that Google doesn’t always use what you set. Sometimes Google decides to pull some text from the page rather than the meta description. There isn’t really anything you can do about this, but don’t worry… Google often tests things to bring people the best results. If you’ve set a meta description Google may switch to that to use instead (or test out) at any point.
Updating Existing Articles to Improve CTR
You can start using these concepts on new articles immediately, but it’s also worth going back and updating old articles. If you haven’t been writing great titles and descriptions it’s a really easy way to get a relatively quick boost in rankings. It’ll take a day to a week (depending on how often Google is indexing your site) for the changes to take place and then if your click through rate (CTR) improves you may see Google boost your article in rankings.
If you’re using an SEO tool like SEO PowerSuite or Moz that tracks rankings you can start off on articles that are just outside of the top 10 or maybe at the bottom of the first page. If you want to track and see how the CTR is moving you can go into Google Analytics under Acquisition > Search Console > Landing Pages and compare the CTR and Average Position before and after the changes. You can also look at which pages have traffic but really low CTR to focus on improving first. It’s not a perfect science (if your rank changes so will the CTR – refer to the chart above) but you can start to see some trends.
Further reading:
- Once you’ve got people coming to your site you’ll want to reduce the bounce rate of your pages to further improve SEO.
- If you want to find the right keywords & track your rankings I recommend checking out my review of SEO PowerTools.

2 Comments
Amit Singh
This is a nice post. I am facing a problem related to Title and Description. Can you please help me to solve this?
Here I have posted- http://wordpress.stackexchange.com/questions/245708/getting-meta-tags-not-found-error
Kyle Larson
In taking a look at it, it seems to be fine from a code perspective. Running the link through validator: https://validator.w3.org/ throws some errors though, specifically about the doctype not being declared. My guess is you’ve got a plugin or template issue where some things aren’t seeing it correctly even though it shows up fine in the code. Maybe with the IE8 type code at the top, not sure…